As the result of a global effort to establish a uniform method of measuring property worldwide, a new international property measurement standard for office buildings — IPMS for Office Buildings — has been created. The IPMS for Office Buildings is compatible with, and complements, Building Owners and Managers Association (BOMA) International’s current office standard Office Buildings: Standard Methods of Measurement (ANSI/BOMA Z65.1—2010). Historically, property has been measured differently throughout the world. According to research by global property firm JLL, depending on the standard used, the area quoted in different markets for an equivalent building could vary by as much as 24 percent. These inconsistencies have led to confusion in markets, and even led businesses to develop their own costly processes for measuring and benchmarking property assets. The work to create the IPMS for Office Buildings was spearheaded by a coalition of more than 50 professional organizations, including BOMA International, and was produced following global consultation by a team of 18 independent industry experts. The IPMS for Office Buildings document can be found at the IPMS website.
Cynthia Hayward
Robotic Pharmacy Aims to Improve Safety
 As one of the nation’s most automated hospital pharmacies, the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) is using robotic technology and electronics with the goal of improving patient safety. Once computers at the pharmacy electronically receive medication orders from UCSF physicians and pharmacists, the robots pick, package, and dispense individual doses of pills. Machines assemble doses onto a thin plastic ring that contains all the medications for a patient for a 12-hour period, which is barcoded. Nurses use barcode readers to scan the medication at patients’ bedsides, verifying it is the correct dosage for the patient. The automated system also compounds sterile preparations of chemotherapy and non-chemotherapy doses and fills IV syringes or bags with the medications.
As one of the nation’s most automated hospital pharmacies, the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) is using robotic technology and electronics with the goal of improving patient safety. Once computers at the pharmacy electronically receive medication orders from UCSF physicians and pharmacists, the robots pick, package, and dispense individual doses of pills. Machines assemble doses onto a thin plastic ring that contains all the medications for a patient for a 12-hour period, which is barcoded. Nurses use barcode readers to scan the medication at patients’ bedsides, verifying it is the correct dosage for the patient. The automated system also compounds sterile preparations of chemotherapy and non-chemotherapy doses and fills IV syringes or bags with the medications.
Substerile Rooms No Longer Advised for the Surgical Suite
In the traditional surgery suite design, operating rooms are grouped around a “sterile core” — from which case carts and sterile supplies are retrieved by the circulating nurse and taken into the operating rooms in preparation for surgery. A “substerile” room was typically placed between two operating rooms to provide “flash” or emergent sterilization of unwrapped items to be used immediately in the operating room. The sterile core often housed a sterilizer as well. Because the items were sterilized in open baskets that could be contaminated by improper handling and exposure during transport, the substerile rooms were placed as close as possible to the operating rooms and the sterile core was considered a restricted area.
Average Age of U.S. Hospitals is Increasing
As a result of reduced spending on renovation and new construction, hospital facilities in the U.S. continue to age. From 2005 to 2008, the average age of a hospital plant was about 9.5 years and then increased dramatically to about 10.5 years from 2009 through 2011. Now, with new data that looks at 2009 through 2013, the average age of a hospital plant has increased further to more than 11 years (11.43) which indicates that investment in hospital facilities continues to be insufficient.
Source: Truven ActionOI® database (www.truvenhealth.com).
3D Mammography is a New Screening and Diagnostic Tool
 Tomosynthesis (also know as 3D mammography) is a revolutionary screening and diagnostic tool designed for early detection of breast cancer that can be done in conjunction with a traditional 2D digital mammogram. Approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011, it is becoming more common in the U.S. During the 3D portion of the exam, the X-ray arm — which uses a comparable radiation dose to a traditional mammogram — sweeps in a slight arc over the breast, taking multiple images in a matter of seconds. A computer then produces a 3D image of the breast tissue in one millimeter slices, providing greater visibility for the radiologist to see tissue details — potentially providing greater accuracy, earlier breast cancer detection, and a decrease in biopsies and recall rates.
Tomosynthesis (also know as 3D mammography) is a revolutionary screening and diagnostic tool designed for early detection of breast cancer that can be done in conjunction with a traditional 2D digital mammogram. Approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011, it is becoming more common in the U.S. During the 3D portion of the exam, the X-ray arm — which uses a comparable radiation dose to a traditional mammogram — sweeps in a slight arc over the breast, taking multiple images in a matter of seconds. A computer then produces a 3D image of the breast tissue in one millimeter slices, providing greater visibility for the radiologist to see tissue details — potentially providing greater accuracy, earlier breast cancer detection, and a decrease in biopsies and recall rates.
Hologic makes the only equipment approved by the FDA. General Electric and Siemens market tomosynthesis equipment overseas and expect to introduce it in the U.S. It is estimated that more than six million American women will undergo tomosynthesis this year.
New Intraoperative Imaging Solutions for Neurosurgery
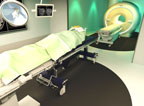 Removing as much of a brain tumor as possible during neurosurgery can make a critical difference in preventing recurrence. Philips has introduced a new MR-OR intraoperative neurosurgery solution based on its Ingenia MR system that allows a neurosurgeon to quickly perform a magnetic resonance imaging (MR or MRI) scan to check the results of a resection during the surgery and remove additional tumor mass if necessary — without first closing the patient’s skull. This reduces the number of repeat surgical procedures, shortens hospital stays, and improves neurosurgery success rates.
Removing as much of a brain tumor as possible during neurosurgery can make a critical difference in preventing recurrence. Philips has introduced a new MR-OR intraoperative neurosurgery solution based on its Ingenia MR system that allows a neurosurgeon to quickly perform a magnetic resonance imaging (MR or MRI) scan to check the results of a resection during the surgery and remove additional tumor mass if necessary — without first closing the patient’s skull. This reduces the number of repeat surgical procedures, shortens hospital stays, and improves neurosurgery success rates.
